ISRO’s Chandrayaan 2: Mission Objectives and Lunar Exploration
Chandrayaan 2, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), is a remarkable lunar mission that aimed to explore the Moon in greater depth. This ambitious project showcased India’s growing prowess in space exploration and scientific research. In this article, we will delve into the mission objectives of Chandrayaan 2 and explore the fascinating world of lunar exploration.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction: Chandrayaan 2 and its Significance
Chandrayaan 2, the second lunar exploration mission by ISRO, aimed to build upon the achievements of its predecessor, Chandrayaan 1. Launched on July 22, 2019, this mission represented India’s determination to expand its scientific knowledge and explore the mysteries of the Moon.
2. Mission Objectives
2.1 Study Lunar Topography
One of the primary objectives of the mission was to study the lunar topography. By capturing high-resolution images and mapping the Moon’s surface, scientists aimed to gain a better understanding of its geological features, such as craters, mountains, and valleys.
2.2 Examine the Lunar Surface
Chandrayaan 2 intended to examine the lunar surface in detail. This involved deploying the lander and rover to collect data on the composition of the soil, rocks, and regolith. By analyzing this data, scientists aimed to unravel the Moon’s geological evolution and its connection to Earth.
2.3 Search for Water Ice
Another crucial objective was to search for water ice on the Moon. The presence of water is essential for future human missions and potential lunar habitation. Chandrayaan 2 carried instruments capable of detecting water molecules in the polar regions of the Moon, where shadowed craters might harbor these valuable resources.
2.4 Analyze the Lunar Exosphere
Studying the lunar exosphere was also part of Chandrayaan 2’s mission objectives. By analyzing the thin atmosphere around the Moon, scientists aimed to understand its composition, variations, and interaction with the solar wind. This research could provide insights into the broader field of planetary exospheres.
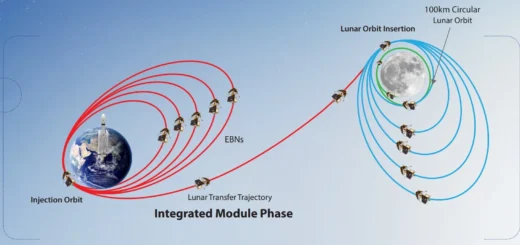
3. The Launch and Journey to the Moon
This mission was launched from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India. The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III) propelled the spacecraft into Earth orbit. After a series of intricate orbital maneuvers, Chandrayaan 2 embarked on its journey to the Moon.
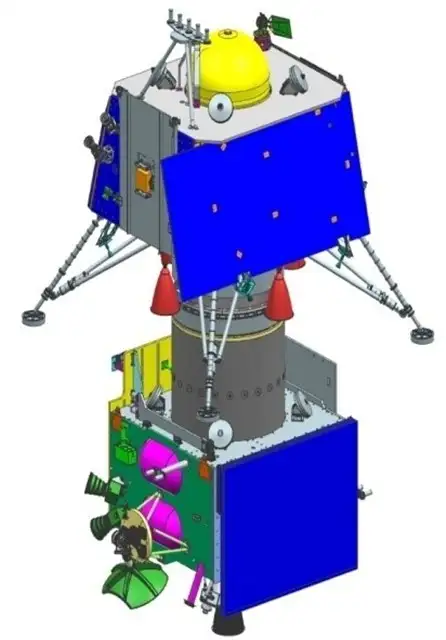
4. The Components of Chandrayaan 2
4.1 The Orbiter
The Orbiter was a crucial component of the mission. It carried a suite of scientific instruments that would operate from a lunar orbit, providing valuable data about the Moon’s surface and atmosphere. The Orbiter played a pivotal role in communication between the lander and Earth.
4.2 The Vikram Lander
Named after Dr. Vikram A. Sarabhai, the renowned Indian physicist and ISRO’s founding chairman, the Vikram Lander was designed to make a soft landing near the Moon’s south pole. It carried instruments to study the lunar surface and transmit data back to Earth.
4.3 The Pragyan Rover
The Pragyan Rover was housed inside the Vikram Lander. Its purpose was to move on the lunar surface and conduct in-situ experiments. Equipped with instruments like a spectrometer and a seismometer, the rover was designed to enhance our understanding of the Moon’s composition and environment.
5. Scientific Discoveries and Achievements
5.1 Mapping the Lunar Surface
Chandrayaan 2’s high-resolution images and data enabled scientists to create detailed maps of the lunar surface. These maps provided valuable insights into the Moon’s geological features and helped identify potential landing sites for future missions.
5.2 Detection of Water Molecules
The mission’s instruments successfully detected water molecules on the lunar surface, particularly in the polar regions. This discovery opened up possibilities for future endeavors, such as utilizing lunar resources for sustainable space exploration and supporting human settlements.
5.3 Lunar Exosphere Analysis
Chandrayaan 2’s analysis of the lunar exosphere revealed valuable information about its composition and dynamics. Understanding the lunar exosphere is crucial for comprehending the interaction between the Moon and its surroundings, including the solar wind and cosmic rays.
6. Challenges Faced and Lessons Learned
Mission faced a significant challenge during the final stages of the mission when communication with Vikram Lander was lost just moments before touchdown. Despite this setback, the mission achieved substantial scientific progress, and ISRO gained valuable insights for future lunar missions.
7. Future Prospects and Collaborative Missions
Chandrayaan 2 laid the foundation for future lunar missions, including ISRO’s upcoming Chandrayaan 3 mission. Additionally, ISRO has collaborated with other space agencies worldwide to further explore the Moon, fostering international cooperation and advancing humanity’s understanding of our celestial neighbor.
8. Conclusion
ISRO’s Chandrayaan 2 mission was an exceptional endeavor that aimed to expand our knowledge of the Moon and its mysteries. Through its mission objectives, the spacecraft successfully studied the lunar topography, examined the lunar surface, searched for water ice, and analyzed the lunar exosphere. Despite encountering challenges, Chandrayaan 2 made significant scientific discoveries and set the stage for future lunar exploration.
9. FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is Chandrayaan 2? Chandrayaan 2 is India’s second lunar exploration mission launched by ISRO.
- What were the objectives of Chandrayaan 2? The objectives of Chandrayaan 2 included studying lunar topography, examining the lunar surface, searching for water ice, and analyzing the lunar exosphere.
- What were the major components of Chandrayaan 2? Chandrayaan 2 consisted of three components named the Pragyan Rover, the Vikram Lander, and an Orbiter.
- Did Chandrayaan 2 discover water on the Moon? Yes, Chandrayaan 2 successfully detected water molecules on the lunar surface, particularly in the polar regions.
- What are the future prospects of Chandrayaan 2? This mission has paved the way for future lunar missions, including Chandrayaan 3, and has established collaborations with other space agencies for further lunar exploration.

1 Response
[…] 3 is India’s third lunar mission and a successor to Chandrayaan 2, which aims to showcase ISRO’s capabilities in safe moon landing and roaming around the moon. […]